BEIJING – As China advances its technological frontiers, National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference member Xu Lijin has positioned intelligent humanoid robots as the next transformative force in industrial and domestic spheres. The robotics expert and Chairman of Wuhu Robot Industry Development Group articulated this vision during the 2025 Two Sessions, urging accelerated integration of these intelligent robots across diverse sectors.
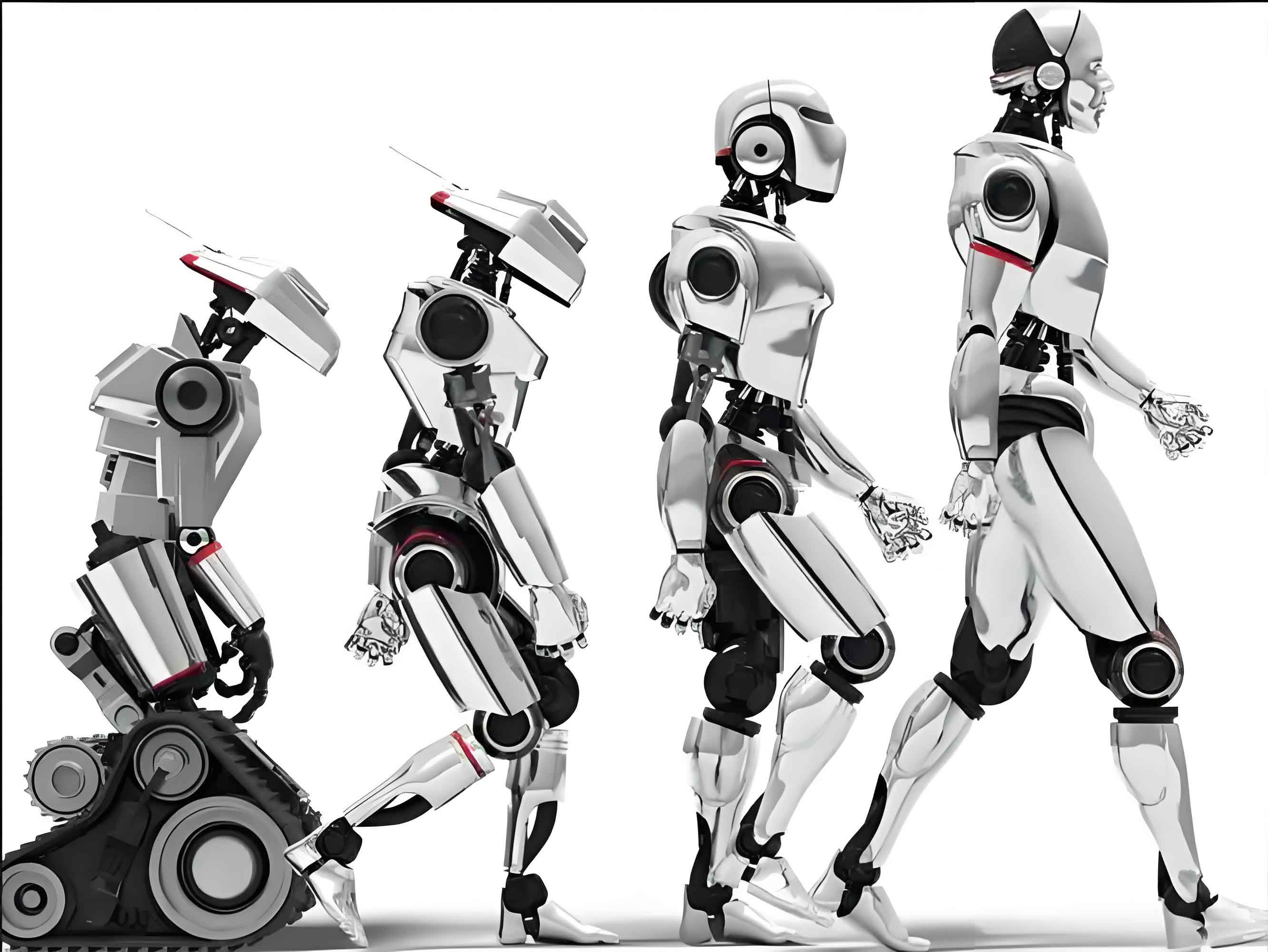
Xu’s advocacy follows notable demonstrations of robotic capabilities, including humanoid robots performing traditional yangko dances during the Spring Festival Gala and the upcoming world’s first humanoid robot half-marathon scheduled for April in Beijing. “Intelligent humanoid robots are evolving into the next-generation smart terminals, following computers, smartphones, and new energy vehicles,” Xu stated, emphasizing their potential to revolutionize productivity and daily life.
The Government Work Report specifically prioritized intelligent robot development as a national strategic focus, signaling strong institutional support. However, Xu identified critical challenges impeding widespread adoption of these sophisticated intelligent robots:
First, fragmented technical approaches hinder universal application. Current development pathways for intelligent robots vary significantly across different usage scenarios, lacking standardized solutions that could enable cross-industry implementation. Manufacturing environments demand different capabilities from healthcare or domestic settings, creating specialized development requirements that slow scalable deployment.
Second, standardization deficits obstruct market growth. The absence of unified technical specifications and certification protocols complicates quality assessment and international compatibility. Without authoritative benchmarks, manufacturers face inconsistent compliance requirements while consumers lack reliable evaluation criteria for these increasingly complex intelligent robots.
Third, safety and ethical considerations require urgent frameworks. As intelligent robots operate in human environments, they present unique challenges including physical safety risks, data privacy vulnerabilities, emotional attachment concerns, and liability ambiguities. These issues become particularly pronounced as robots develop more sophisticated anthropomorphic features.
To overcome these barriers, Xu proposed concrete measures:
- Establish pilot programs in accessible, high-demand sectors to generate implementation data, creating standardized scenario libraries for accelerated algorithm refinement and product optimization of intelligent robots.
- Expedite development of universal technical standards while creating national-level testing and certification centers to ensure quality control and facilitate international standards reciprocity for intelligent robots.
- Implement comprehensive safety and ethical regulations, including mandatory product liability insurance requirements for manufacturers deploying intelligent robots in public or private settings.
“Intelligent robots represent not just technological advancement but a fundamental shift in human-machine interaction,” Xu emphasized. “Strategic integration of these intelligent robots across industries could redefine manufacturing efficiency, elderly care, hazardous environment operations, and household assistance.”
Industry analysts note that China’s intelligent robot sector has progressed from imitation-based innovation to pioneering original development. This transition positions the country advantageously in the global race for intelligent robot supremacy, though core components and specialized materials remain development priorities.
International observers highlight that China’s approach to intelligent robot deployment combines industrial pragmatism with ethical foresight. The dual focus on commercial scalability through pilot programs and preemptive risk mitigation through insurance requirements creates a balanced development template for intelligent robots.
As Beijing prepares for the landmark robot marathon, the event symbolizes both technological achievement and the persistent challenges in endurance and reliability that intelligent robots must overcome. Each participating unit will demonstrate current capabilities while exposing limitations in energy management, terrain adaptation, and failure recovery – precisely the areas Xu’s proposals aim to address.
The convergence of policy support, technological maturation, and ethical frameworks could potentially accelerate the timeline when intelligent robots transition from specialized tools to ubiquitous assistants. With global markets watching China’s strategic moves, the implementation of Xu’s recommendations may determine how quickly these intelligent robots evolve from exhibition showcases to essential components in factories, hospitals, and homes worldwide.
| Phase | Technological Focus | Key Challenges | Industrial Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prototype Development | Basic mobility and object manipulation | Hardware durability and power efficiency | Laboratory testing environments |
| Specialized Application | Environment-specific adaptation | Scenario fragmentation and customization costs | Niche industrial implementations |
| General Integration | Cross-platform interoperability | Standardization and safety certification | Broad commercial deployment |
| Ubiquitous Adoption | Affordability and user interface refinement | Ethical frameworks and public trust | Household and consumer applications |
Technical experts concur that resolving the standardization dilemma represents the most immediate catalyst for scaling intelligent robot deployment. Uniform communication protocols, safety interlocks, and performance metrics would enable component modularity and mass production economies. The proposed national certification center could become the authoritative institution validating these intelligent robots for diverse operating environments.
Consumer advocacy groups have welcomed the emphasis on ethical safeguards, particularly regarding data security for domestic intelligent robots. As these devices increasingly process personal information and interact with vulnerable populations, the insurance requirement proposal establishes financial accountability mechanisms alongside technical standards.
Global technology competitors are closely monitoring China’s policy developments, recognizing that intelligent robot leadership could reshape manufacturing competitiveness and service industry paradigms. Nations with aging populations particularly anticipate cost-effective care solutions from next-generation intelligent robots capable of physical assistance and social interaction.
With the Two Sessions spotlighting robotics advancement, Xu’s comprehensive roadmap addresses both the technical foundations and societal implications of the coming wave of intelligent robots. As development accelerates, the integration of these sophisticated intelligent robots across factories, warehouses, hospitals, and households appears increasingly inevitable – transforming from technological novelty to essential infrastructure in the global economy.
